Constructing Robust Affinity Graphs for Spectral Clustering CVPR'14
Introduction
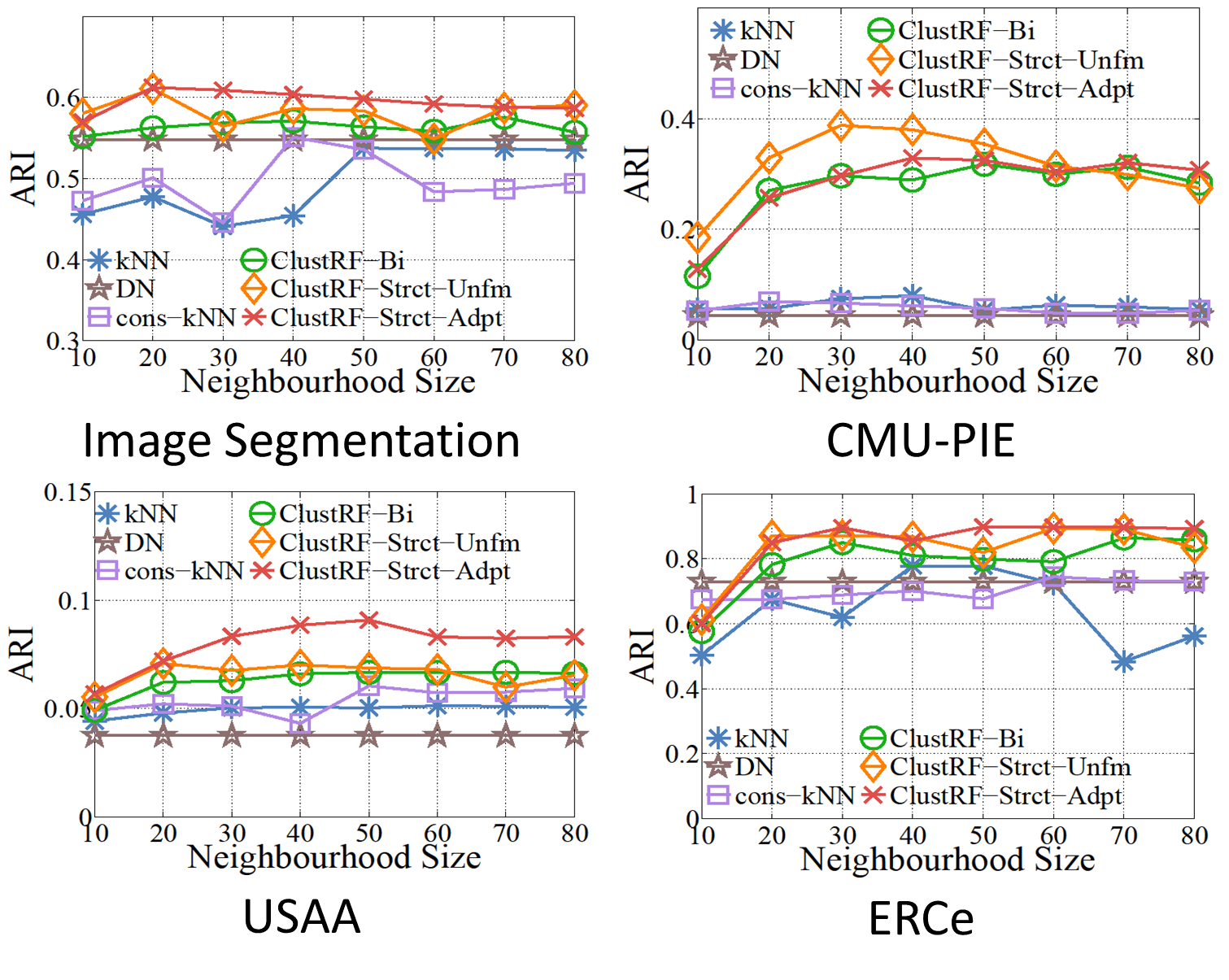
Spectral clustering requires robust and meaningful affinity graphs as input in order to form clusters with desired structures that can well support human intuition. To construct such affinity graphs is non-trivial due to the ambiguity and uncertainty inherent in the raw data. In contrast to most existing clustering methods that typically employ all available features to construct affinity matrices with the Euclidean distance, which is often not an accurate representation of the underlying data structures, we propose a novel unsupervised approach to generating more robust affinity graphs via identifying and exploiting discriminative features for improving spectral clustering. Specifically, our model is capable of capturing and combining subtle similarity information distributed over discriminative feature subspaces for more accurately revealing the latent data distribution and thereby leading to improved data clustering, especially with heterogeneous data sources. We demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed approach on challenging image and video datasets.
Contribution Highlights
We formulate a unified and generalised data similarity inference framework based on the unsupervised clustering random forest with three innovations:- Instead of considering the complete feature space as a whole, the proposed model is designed to avoid less informative features by measuring between-sample proximity via discriminative feature subspaces, yielding similarity graphs that better express the underlying semantic structure in data.
- We relax the Euclidean assumption for data similarity inference by following the information-theoretic definition of data similarity that different similarities can be induced from a given sample pair if distinct propositions are taken or different questions are asked about data commonalities.
- The pairwise affinity matrix generated by the proposed model automatically possesses the local neighbourhood. Thus, no additional Gaussian kernel is needed to enforce locality.
Citation
Images
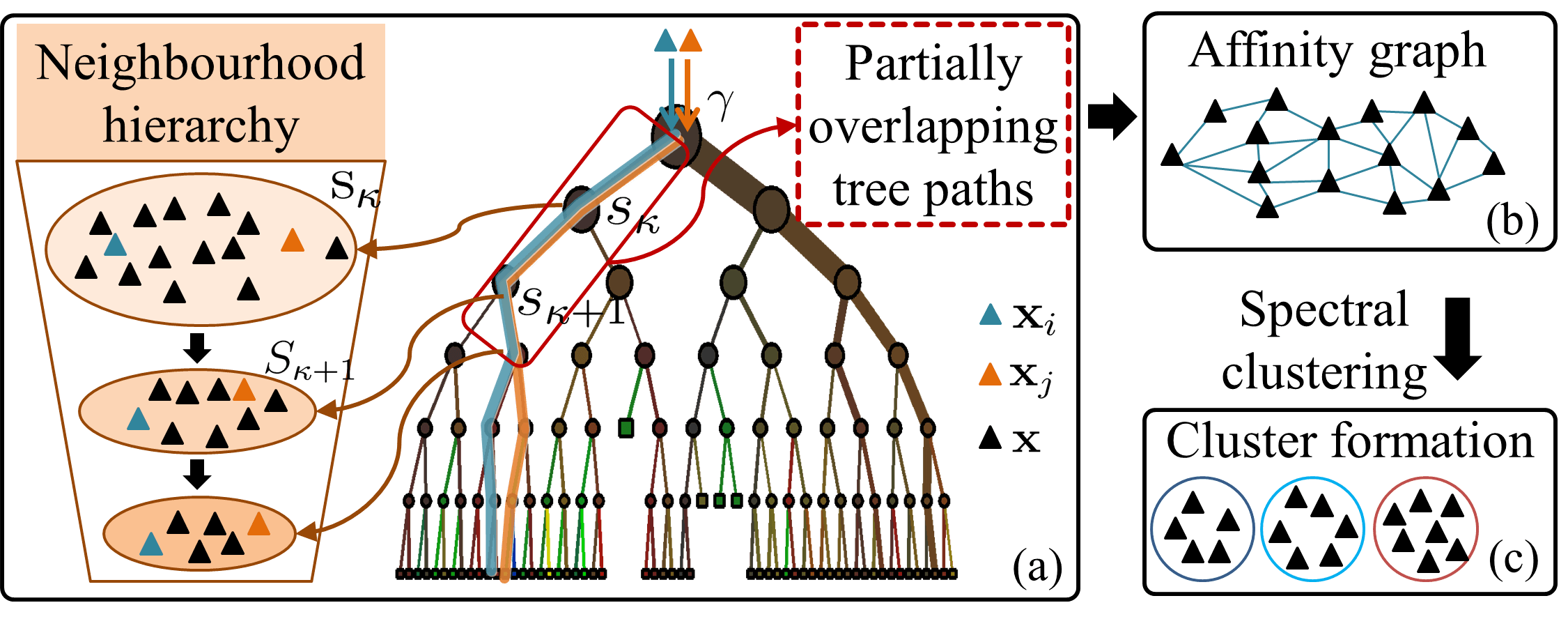
Overview of our approach:
The proposed affinity graph construction approach is built upon clustering random forests, with a few important merits:
- Our model is purely unsupervised without requiring any ground truth annotations, since it is based on clustering forests rather the more popular supervised classification or regression random forests
- By virtue of the random subspace feature selection during training forests, the pairwise affinity matrix generated by our model is less susceptible to corruption of noisy and irrelevant features.
- Each decision tree in the forest hierarchically encodes an exhaustive set of comparative tests or split functions, which implicitly define different notions of between-sample similarities. Our model is capable of extracting and combining these subtle similarities at distributed discriminative subspaces for learning robust pairwise affinity matrices.
Datasets and Codes
An indoor dataset collected from a university campus for physical event understanding of long video streams.
Details ...C++ codes with MATLAB wrapper for unsupervised clustering forest. It can construct robust affinity graph for spectral clustering or manifold ranking. Apart from the proposed approach, the code also includes binary affinity described in A. Criminisi and J. Shotton, Decision Forests for Computer Vision and Medical Image Analysis, Springer 2013. A demo is included.